How a Vein Becomes a Varicose Vein or Spider Vein
San Antonio Vein Center – Explains Spider & Varicose Veins
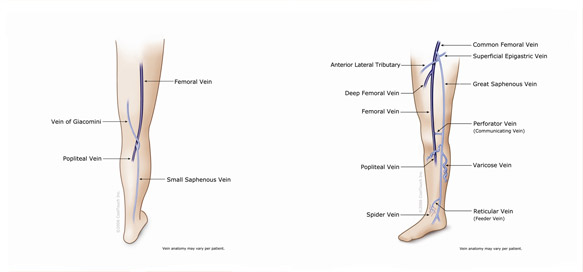
Veins that are present in the skin or the fatty tissue below the skin make up the superficial vein system. The superficial vein system is extremely variable with many interconnections.Most people have a large vein along the middle side of the leg that connects with the deep vein system at the groin. It is called the great saphenous vein and is most well-known as the vein that is used for coronary artery bypass operations. It usually has several branches called tributaries that often become bulging varicose veins if the valves in the great saphenous vein fail.
Another vein called the small saphenous vein runs from the back of the ankle up the middle of the calf to the back of the knee. Tributaries from the small saphenous vein may also cause varicose veins in the lower leg if the valves in the small saphenous vein fail.
Medium and small superficial veins collect blood and return it to the larger superficial veins. It is these veins that become spider veins and visible reticular (blue) veins.
Another type of vein called a perforating vein is responsible for channeling blood from the superficial system into the deep system. These veins connect the great and small saphenous veins along their paths to the deep veins. However, perforating veins may be found almost anywhere on the legs connecting superficial veins to deep veins. A failed perforating vein called an incompetent perforating vein or IPV commonly leads to varicose veins that seem to “come from nowhere” until the IPV is located by a duplex ultrasound exam. They also frequently are the cause of persistent varicose veins after larger incompetent veins have been treated.
In summary, no two people have the same superficial vein system. The only way to determine the pattern of vein failure is by a thorough duplex ultrasound exam. Thus the ultrasonographer ultimately discovers the pattern of blood flow in the superficial vein system and the location of any problems in the system. This is the keystone of effective vein treatment.